2.2 POJA-L1104
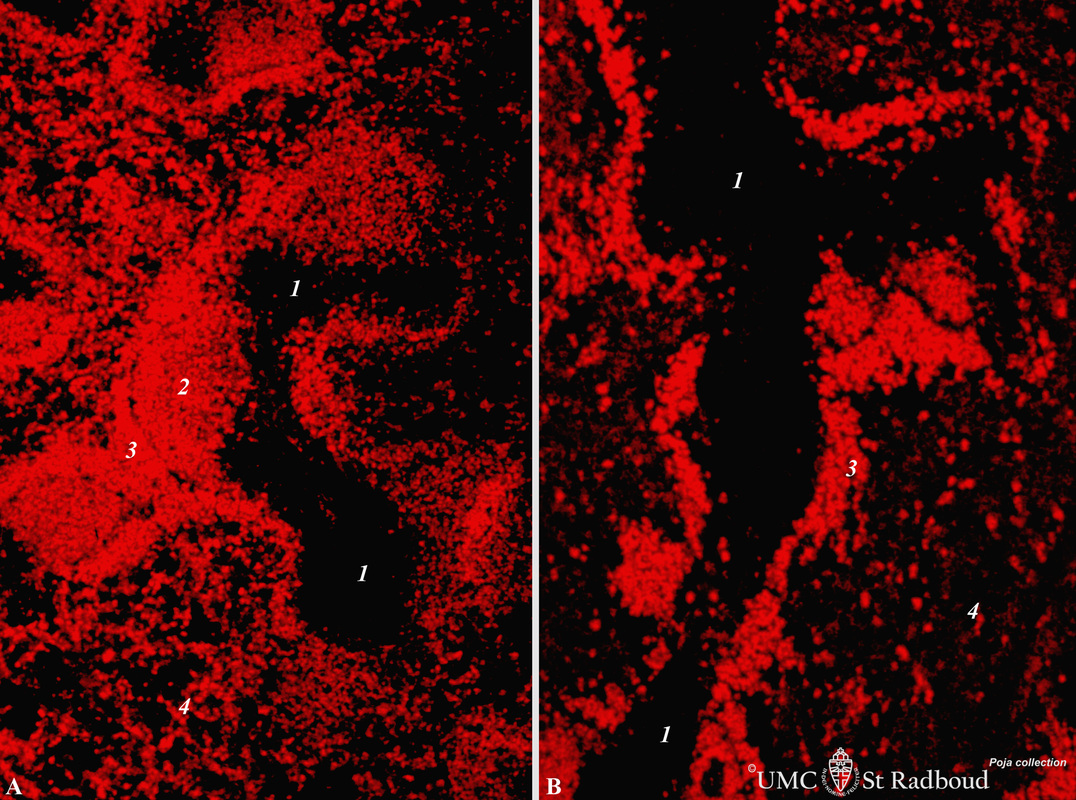
Title: Immunofluorescence localization of B cells in spleen (rat)
Description: Stain: Vector red immunofluorescence using mark-1 antibody against B cells.
(A): Normal rat spleen. (1) The dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphocyte sheath) filled with T cells. (2) Red stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3). Note that B cells are also spread in the red pulp area (4).
(B): 4 days after a single treatment with cyclophosphamide the number of red stained B cells are considerably reduced in the follicles (2) and marginal zones (3), but also in the red pulp (4). The cyclophosphamide treatment causes a temporarily severe reduction of the immune response to antigens, partly to the reduced levels of B cells.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organs, spleen, B cells, rat, immunofluorescence, histology, POJA collection
Title: Immunofluorescence localization of B cells in spleen (rat)
Description: Stain: Vector red immunofluorescence using mark-1 antibody against B cells.
(A): Normal rat spleen. (1) The dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphocyte sheath) filled with T cells. (2) Red stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3). Note that B cells are also spread in the red pulp area (4).
(B): 4 days after a single treatment with cyclophosphamide the number of red stained B cells are considerably reduced in the follicles (2) and marginal zones (3), but also in the red pulp (4). The cyclophosphamide treatment causes a temporarily severe reduction of the immune response to antigens, partly to the reduced levels of B cells.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organs, spleen, B cells, rat, immunofluorescence, histology, POJA collection