7.3 POJA-L1382+1278+1406
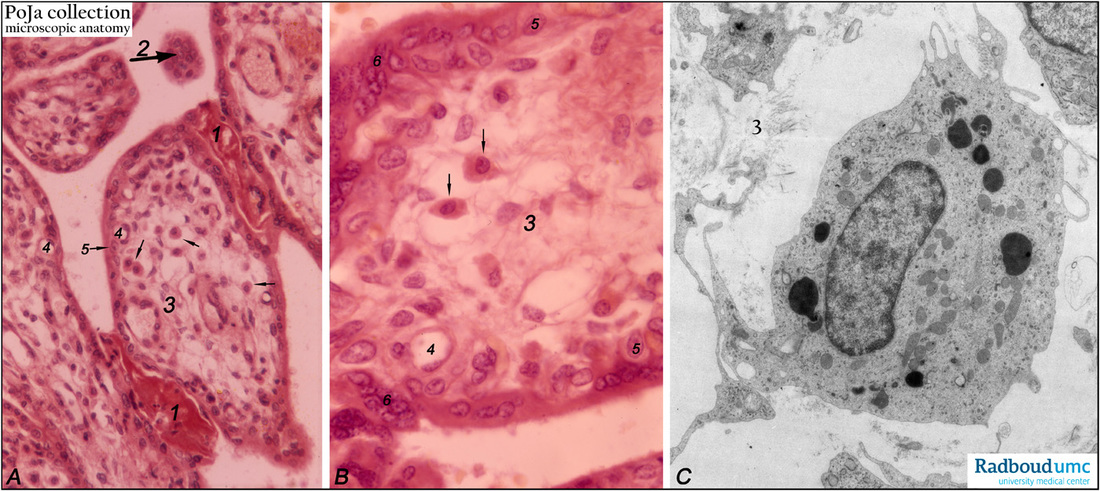
Title: Tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy)
Description: (A) Lower and (B) higher magnification. Stain: Hematoxylin – azophloxine.
(C) electron microscopy of Hofbauer cell.
(A, B) show tertiary villi and intervillous spaces. Squeezed between villi fibrinoid clots (1). The large arrow (2) points to either a detached, free circulating large STC (syncytiotrophoblast) in the intervilllous space or a cross-section of the tip of a sprout. The villi show embryonic connective tissue (3). Small unnumbered arrows point to wandering phagocytic Hofbauer cells in (A, B).
An electron micrograph of this placental macrophage cell type is shown in (C). The cell is CD68+ and likely functions also as an antigen-presenting cell (APC). The Hofbauer cell is only faintly eosinophilic and highly vacuolated, with dark granules in electron microscopy shown in (C). The granules are also considered as carriers of nutrients and Fas Ligand obtained from STCs. Capillaries (4) are distinct. The cytotrophoblast (CTC, Langhans) lining (5) remains covered by the postmitotic multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 6). Distinct nuclear accumulation in the STC are so-called syncytiotroblast knots (6) eventually resulting in sprouts of syncytiotrophoblastic islands.
Background: Up to the end of the 4th gestational month, the trophoblast covering is two-layered by the outer STCs and the inner CTCs.
Keywords/Mesh: placenta, chorionic villi, Hofbauer cell, fibrinoid, syncytiotrophoblast, trophoblast, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection.
Title: Tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy)
Description: (A) Lower and (B) higher magnification. Stain: Hematoxylin – azophloxine.
(C) electron microscopy of Hofbauer cell.
(A, B) show tertiary villi and intervillous spaces. Squeezed between villi fibrinoid clots (1). The large arrow (2) points to either a detached, free circulating large STC (syncytiotrophoblast) in the intervilllous space or a cross-section of the tip of a sprout. The villi show embryonic connective tissue (3). Small unnumbered arrows point to wandering phagocytic Hofbauer cells in (A, B).
An electron micrograph of this placental macrophage cell type is shown in (C). The cell is CD68+ and likely functions also as an antigen-presenting cell (APC). The Hofbauer cell is only faintly eosinophilic and highly vacuolated, with dark granules in electron microscopy shown in (C). The granules are also considered as carriers of nutrients and Fas Ligand obtained from STCs. Capillaries (4) are distinct. The cytotrophoblast (CTC, Langhans) lining (5) remains covered by the postmitotic multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 6). Distinct nuclear accumulation in the STC are so-called syncytiotroblast knots (6) eventually resulting in sprouts of syncytiotrophoblastic islands.
Background: Up to the end of the 4th gestational month, the trophoblast covering is two-layered by the outer STCs and the inner CTCs.
Keywords/Mesh: placenta, chorionic villi, Hofbauer cell, fibrinoid, syncytiotrophoblast, trophoblast, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection.