1.1 POJA-L650
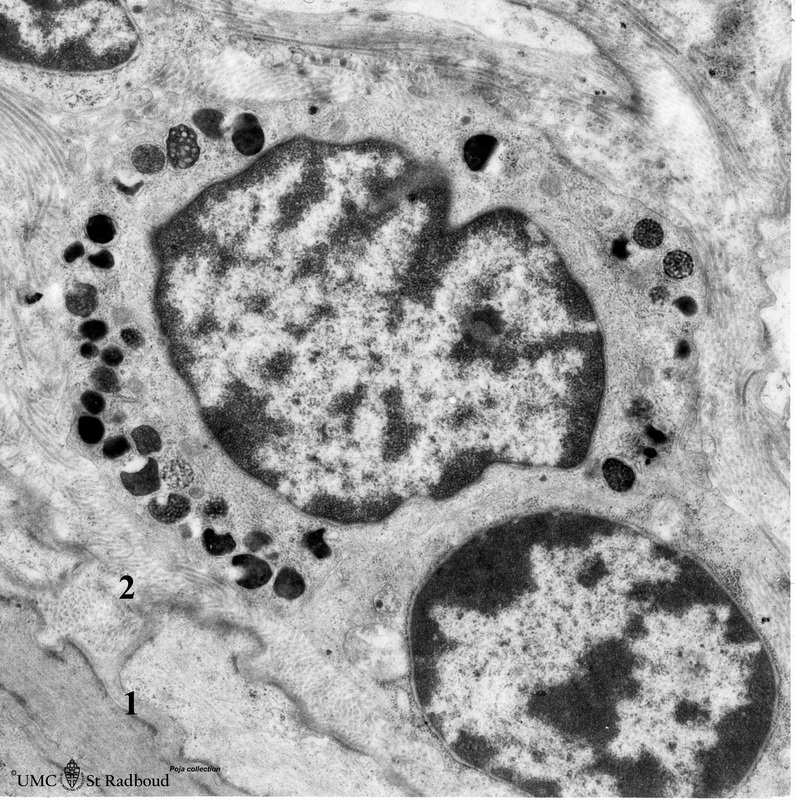
Title: Mast cell (lung, dog)
Description: Electron microscopy.
This mucosal mast cell of the lung is localized in the vicinity of a blood vessel. Notice the smooth muscle cells (1) of a small arteriole and collagen fibers (2). Most obvious is the presence of granules varying in shape and size.
These membrane-bound vesicles (so-called compound granules) show a metachromatic reaction in light microscopy and ultrastructurally a granule exhibits a heterogeneous content (different with species) e.g. osmiophilic granular, filamentous, whorl-like substances.
These structures contain among others heparin, histamine, enzymes such as tryptase, (superoxide dismutase, b-hexosaminidase) factors such as neutrophil – and eosinophil-chemotactic factors, vasoactive mediators. The content of the granules varies strongly with different species (rodent, human).
A second subset of mast cells is the connective tissue mast cell. In rodents the major granule proteoglycan is heparin (and histamine).
Mast cells are activated by cross-linking of the IgE-receptors occupied by IgE and by allergen. Activation of mast cells results in three types of response: (1) secretion of preformed contents of their granules (exocytosis); (2) synthesis and secretion of lipid mediators; (3) synthesis and secretion of cytokines. Eventually the degranulation can result in an immediate hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reaction.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, mast cell, basophilic granulocyte, metachromasia, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Mast cell (lung, dog)
Description: Electron microscopy.
This mucosal mast cell of the lung is localized in the vicinity of a blood vessel. Notice the smooth muscle cells (1) of a small arteriole and collagen fibers (2). Most obvious is the presence of granules varying in shape and size.
These membrane-bound vesicles (so-called compound granules) show a metachromatic reaction in light microscopy and ultrastructurally a granule exhibits a heterogeneous content (different with species) e.g. osmiophilic granular, filamentous, whorl-like substances.
These structures contain among others heparin, histamine, enzymes such as tryptase, (superoxide dismutase, b-hexosaminidase) factors such as neutrophil – and eosinophil-chemotactic factors, vasoactive mediators. The content of the granules varies strongly with different species (rodent, human).
A second subset of mast cells is the connective tissue mast cell. In rodents the major granule proteoglycan is heparin (and histamine).
Mast cells are activated by cross-linking of the IgE-receptors occupied by IgE and by allergen. Activation of mast cells results in three types of response: (1) secretion of preformed contents of their granules (exocytosis); (2) synthesis and secretion of lipid mediators; (3) synthesis and secretion of cytokines. Eventually the degranulation can result in an immediate hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reaction.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, mast cell, basophilic granulocyte, metachromasia, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection