14.1 POJA-L6057+6059+6060+6061 Electron micrographs of T-tubules and triads in striated muscle (mouse)
|
14.1 POJA-L6057+6059+6060+6061 Electron micrographs of T-tubules and triads in striated muscle (mouse)
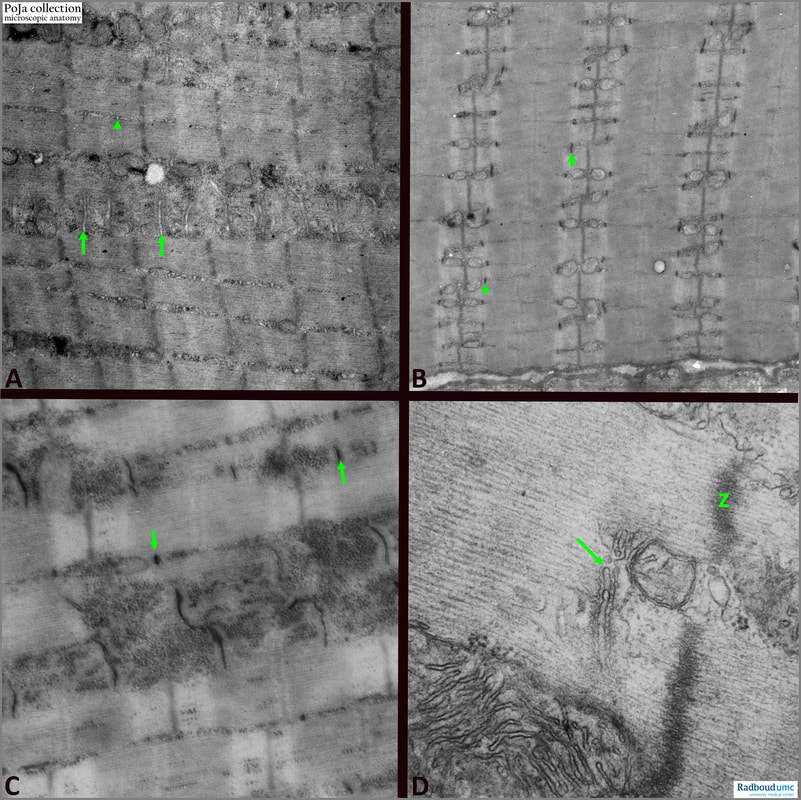
Title: Electron micrographs of T-tubules and triads in striated muscle (mouse) Description: (A): Striated muscle with parallel arranged sarcomeres. Arrows/arrowhead indicate the T-tubules being deep invaginations of the sarcolemma into the muscle fibres at the level of the A-I band junctions. They serve for propagating the electric stimulus into the myofilaments. (B):The use of ferrocyanide in the fixation fluid accentuates the black T-tubules (arrows/arrowhead). The light bulbs are mitochondria. (C): Idem, magnified, T-tubules (arrows). The vesicle-like structures at both sites of the dark T-tubules are parts of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (not in focus). Note the numerous dark stained glycogen granules. (D): (arrow) a triad of one transverse tubule and two terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Between the tubule and cisternae small dots indicate pikes or feet (ryanodine receptors for intracellular calcium canal localisation). The release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is initiated by depolarisation of the membrane of the T-tubule. (Z) is dense Z-line. See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, myofibre, A-band, I-band, Z-line, mitochondrion, T-tubule, triad, ryanodine receptor, electron microscopy, POJA collection |