POJA-L2834+2835+2836
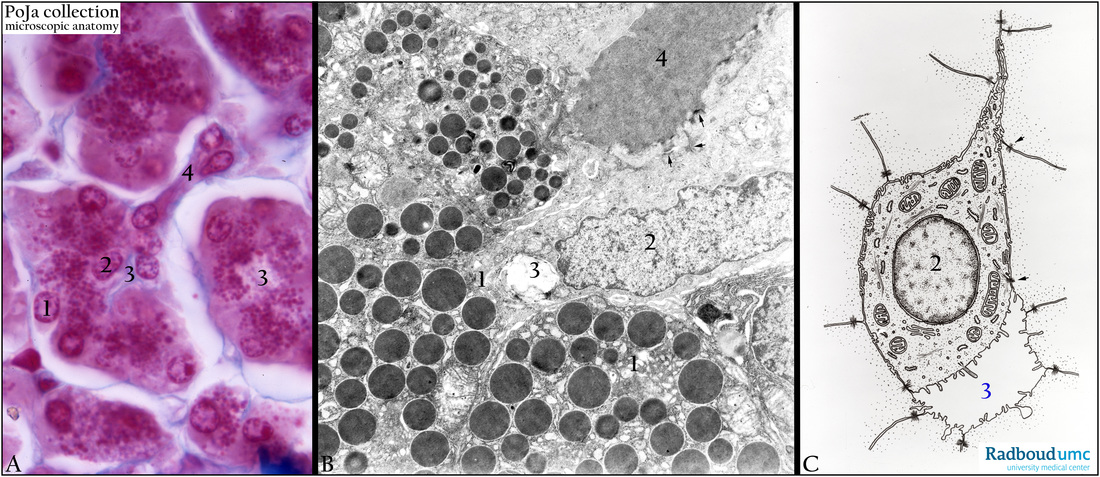
Title: Pancreatic acinus with intercalated duct (human)
Description: Stain: (A) Azan. (B) Electron micrograph. (C) Scheme centroacinar cell.
The acini in (A) consist of secretory granulated cells (1) arranged around a small lumen (3). The secretory product is exported through an intercalated duct (4) that originates within the lumen as a centroacinar cell (2).
In the electron micrograph (B) the secretory granules are electron-densely stained. The centroacinar cell (2) is connected to the cells of the intercalated duct (4) by desmosomes (arrows). The centroacinar cells mainly produce a clear fluid (bicarbonate) thus lacking secretory granules. The intercalated duct cells secrete water and bicarbonate ions regulated by secretin. The latter hormone as well as cholecystokinin is produced by enteroendocrine cells of duodenum/jejunum when chyme enters the small intestine.
Keywords/Mesh: pancreas, exocrine, centroacinar cell, intercalated duct, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Pancreatic acinus with intercalated duct (human)
Description: Stain: (A) Azan. (B) Electron micrograph. (C) Scheme centroacinar cell.
The acini in (A) consist of secretory granulated cells (1) arranged around a small lumen (3). The secretory product is exported through an intercalated duct (4) that originates within the lumen as a centroacinar cell (2).
In the electron micrograph (B) the secretory granules are electron-densely stained. The centroacinar cell (2) is connected to the cells of the intercalated duct (4) by desmosomes (arrows). The centroacinar cells mainly produce a clear fluid (bicarbonate) thus lacking secretory granules. The intercalated duct cells secrete water and bicarbonate ions regulated by secretin. The latter hormone as well as cholecystokinin is produced by enteroendocrine cells of duodenum/jejunum when chyme enters the small intestine.
Keywords/Mesh: pancreas, exocrine, centroacinar cell, intercalated duct, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection