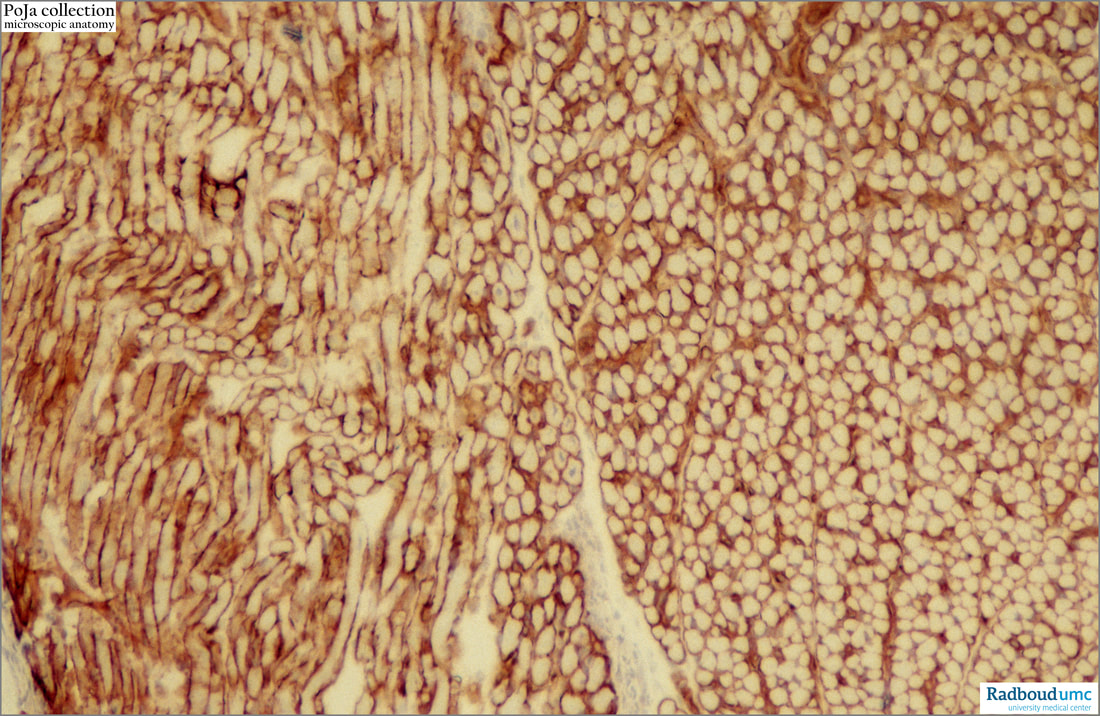
14.1 POJA-L6107 Immunoperoxidase staining for laminin in skeletal muscle (postnatal rat)
 14.1 POJA-L6107 Laminin staining of skeletal muscle
14.1 POJA-L6107 Laminin staining of skeletal muscle
14.1 POJA-L6107 Immunoperoxidase staining for laminin in skeletal muscle (postnatal rat)
Title: Immunoperoxidase staining for laminin in skeletal muscle (postnatal rat)
Description:
Laminin, a large (400–900 kDa) heterotrimeric extracellular glycoprotein, is a major constituent of the basal lamina together with type IV collagen. Laminin-211 (formerly named merosin) is the most abundant laminin isoform in the basal lamina of adult skeletal muscle. However, additional laminin isoforms are also present during myogenesis and at junctional regions of the muscle fibres such as the neuromuscular junction and the myotendinous junction.
The image shows the laminin localisation all around each muscle fibre up to the interstitial tissue. It follows the distribution of collagen IV in the longitudinal section (left side) and cross section (right side).
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, basal lamina, laminin, glycoprotein, histology, POJA-collection
Description:
Laminin, a large (400–900 kDa) heterotrimeric extracellular glycoprotein, is a major constituent of the basal lamina together with type IV collagen. Laminin-211 (formerly named merosin) is the most abundant laminin isoform in the basal lamina of adult skeletal muscle. However, additional laminin isoforms are also present during myogenesis and at junctional regions of the muscle fibres such as the neuromuscular junction and the myotendinous junction.
The image shows the laminin localisation all around each muscle fibre up to the interstitial tissue. It follows the distribution of collagen IV in the longitudinal section (left side) and cross section (right side).
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, basal lamina, laminin, glycoprotein, histology, POJA-collection
