4.1.1 POJA-L3923+3924
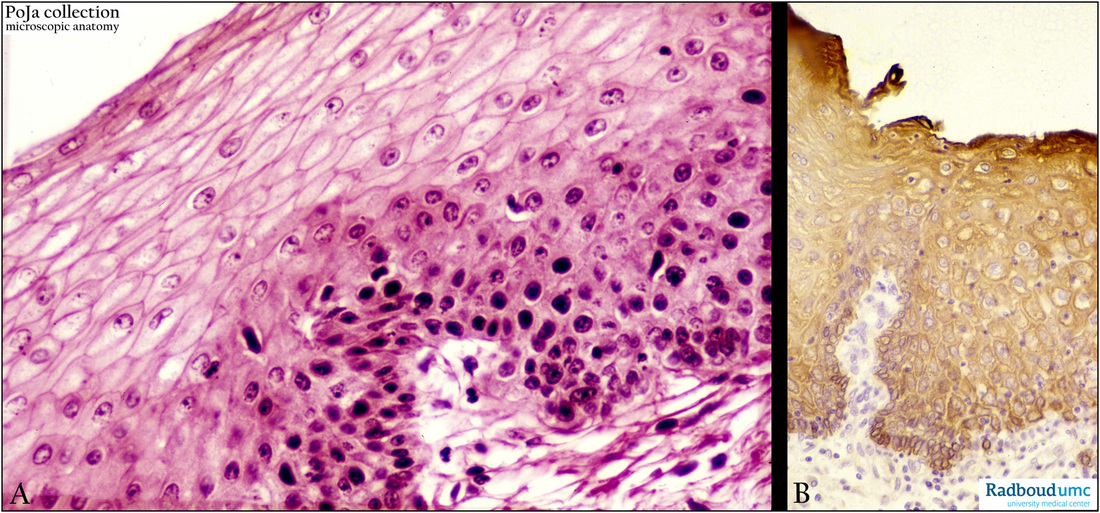
Title: Epithelial lining of the esophagus (human)
Description: Stain: (A) Hematoxylin-eosin. (B) Anti-polykeratin antibody immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin reaction (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstaining.
The epithelium of the esophagus is a multilayered non-keratinizing squamous epithelium (A) that is well enforced with keratin fibers (B). The cells of the upper layers are flattened, while the basal cells are rather cuboidal resting on a basal lamina. Note that many lymphoid cells (dark small nuclei) have invaded from the lamina propria area into and between the basal cells of the epithelium. They function as immunological surveyors for protection against allergens and microbial infections.
Keywords/Mesh: esophagus, squamous epithelium, keratin, polykeratin antibody, histology, POJA collection
Title: Epithelial lining of the esophagus (human)
Description: Stain: (A) Hematoxylin-eosin. (B) Anti-polykeratin antibody immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin reaction (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstaining.
The epithelium of the esophagus is a multilayered non-keratinizing squamous epithelium (A) that is well enforced with keratin fibers (B). The cells of the upper layers are flattened, while the basal cells are rather cuboidal resting on a basal lamina. Note that many lymphoid cells (dark small nuclei) have invaded from the lamina propria area into and between the basal cells of the epithelium. They function as immunological surveyors for protection against allergens and microbial infections.
Keywords/Mesh: esophagus, squamous epithelium, keratin, polykeratin antibody, histology, POJA collection