4.4.1 POJA-L-4200
Title: Scheme of the pancreas (human)
Description:
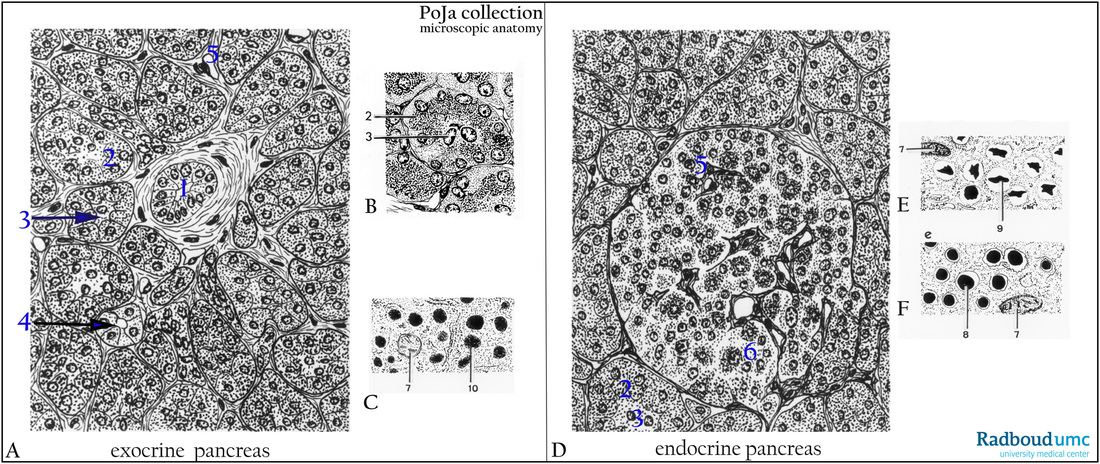
(A, B, C): Exocrine glands of the pancreas. The exocrine part of the pancreas consists of purely serous glands. (1) Interlobular duct. (2) Serous secretory basophilic cells. (3, arrow) Clear centroacinar cell. (4, arrow) Intralobular duct or intercalated duct. (5) Capillary. (7) Mitochondrion. (10) Serous secretory granule. The exocrine gland is constructed as lobes, and each lobe contains ducts and acini. The acinar cells produce secretory zymogen granules containing digestive enzymes such as carboxypeptidase, trypsin (chymotrypsin), nucleases, amylases and lipases released as inactive forms, which become activated subsequently in the lumen of the digestive tract. The pancreas secretion is affected by duodenal hormones secretin and cholecystokinin. Secretin stimulates the bicarbonate production in the centroacinar cells and in the cells of the intercalated ducts. Cholecystokinin stimulates the acinar cells.
(D, E, F): Endocrine part of the pancreas (the islets of Langerhans). Centrally located in the drawing an endocrine Langerhans islet consisting of clusters of endocrine cells (6) of three types, α-, β- and δ-cells. The α-cells produce glucagon that elevates the blood glucose level via liver glycogen. The β-cells produce insulin that lowers the blood glucose level in favor of formation of glycogen in liver and muscles, while the δ-cells generate somatostatin that modulates the release of insulin and glucagon. Usually the islets of Langerhans consist of about 20% α-cells, 60-80% β-cells and 8% δ-cells. A fourth cell type is called PP-cell and produces pancreas polypeptide acting as gastrin antagonist lowering the HCl production in the stomach. (8) Insulin granule with a clear zone surrounding the dense granule. (9) β-granule with crystalline inclusion. Note the numerous capillaries (fenestrated in electron microscopy) within the islet.
Keywords/Mesh: pancreas, islets of Langerhans, exocrine, endocrine, glucagon-secreting cells, insulin-secreting cells, somatostatin-secreting cells, pancreatic ducts, histology, POJA collection
Title: Scheme of the pancreas (human)
Description:
(A, B, C): Exocrine glands of the pancreas. The exocrine part of the pancreas consists of purely serous glands. (1) Interlobular duct. (2) Serous secretory basophilic cells. (3, arrow) Clear centroacinar cell. (4, arrow) Intralobular duct or intercalated duct. (5) Capillary. (7) Mitochondrion. (10) Serous secretory granule. The exocrine gland is constructed as lobes, and each lobe contains ducts and acini. The acinar cells produce secretory zymogen granules containing digestive enzymes such as carboxypeptidase, trypsin (chymotrypsin), nucleases, amylases and lipases released as inactive forms, which become activated subsequently in the lumen of the digestive tract. The pancreas secretion is affected by duodenal hormones secretin and cholecystokinin. Secretin stimulates the bicarbonate production in the centroacinar cells and in the cells of the intercalated ducts. Cholecystokinin stimulates the acinar cells.
(D, E, F): Endocrine part of the pancreas (the islets of Langerhans). Centrally located in the drawing an endocrine Langerhans islet consisting of clusters of endocrine cells (6) of three types, α-, β- and δ-cells. The α-cells produce glucagon that elevates the blood glucose level via liver glycogen. The β-cells produce insulin that lowers the blood glucose level in favor of formation of glycogen in liver and muscles, while the δ-cells generate somatostatin that modulates the release of insulin and glucagon. Usually the islets of Langerhans consist of about 20% α-cells, 60-80% β-cells and 8% δ-cells. A fourth cell type is called PP-cell and produces pancreas polypeptide acting as gastrin antagonist lowering the HCl production in the stomach. (8) Insulin granule with a clear zone surrounding the dense granule. (9) β-granule with crystalline inclusion. Note the numerous capillaries (fenestrated in electron microscopy) within the islet.
Keywords/Mesh: pancreas, islets of Langerhans, exocrine, endocrine, glucagon-secreting cells, insulin-secreting cells, somatostatin-secreting cells, pancreatic ducts, histology, POJA collection