13.1 POJA-L4511+4513+4505+4514+4515
Title: Lipofuscin and endocrine granules in myocardiocytes
Description:
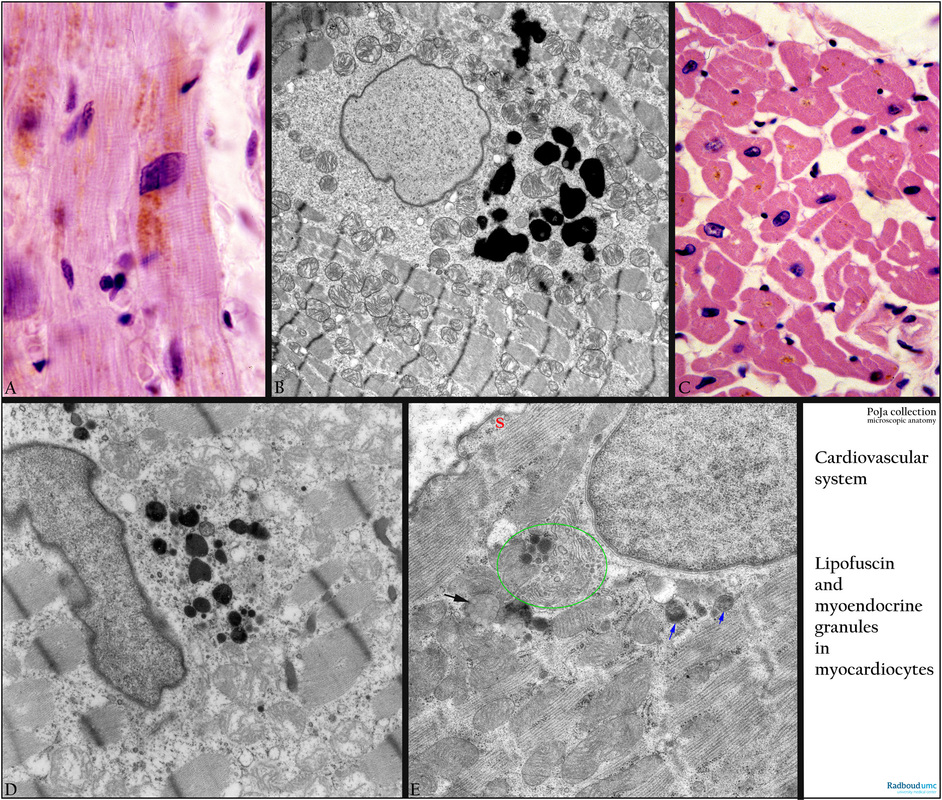
(A): Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy, senium human. A large amount of yellow-brown-stained lipofuscin is present in the vicinity of the nucleus. Note the large nucleus (frequently anisokaryosis).
(B): Cardiocyte in ventricle, electron microscopy, human. Electron-dense granules (dark) of irregular diameter represent lipofuscin in the paranuclear area. Swollen mitochondria and partly disrupted bundles of myofilaments and glycogen surrounding the nucleus are observed (biopsy during open heart operation). Note the banding of the sarcomeres.
(C): Cross-sectioned cardiocytes of the ventricle, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy (swollen interstitium), human. Note irregular outline of the branching and anastomosing cells. Not every cross-sectioned cardiocyte contains a nucleus. Yellow-brown stained pigment is lipofuscin located at the nuclear poles in the cell.
(D): Cardiocyte in ventricle, electron microscopy, monkey. Paranuclearly electron-dense (dark) lipofuscin of varying diameters.
(E): Cardiocyte in atrium, electron microscopy, rat. This special type of myoendocrine cell shows a distinct Golgi area (green encircled) close to the nucleus that reveals few dense secretion granules. These granules will be exported by exocytosis and are known as polypeptides i.a. atrial natriuretic polypeptide (ANP) or BNP (brain natriuretic polypeptide) or CDD (cardiodilatine). (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.06.008). Arrow (black) to lipofuscin and arrows (blue) to lysosomes. (S) Peripheral cytoplasm with caveolae and without myofilaments.
Background: Generally, three cell types are distinguished in the myocardium. (1) Contractile cardiocytes contributing to the pumping action of the heart. (2). Myoendocrine cardiocytes producing polypeptides (e.g. ANP, BNP etc.). (3). Nodal cardiocytes controlling the rhythmic heart contraction, and which are specialised cells found in the sinoatrial node (at the junction right atrium and superior vena cava) as well as in the atrioventricular node (subendocardial in atrial and ventricular septa).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myoendocrine cell, ANP, BNP, lipofuscin, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Lipofuscin and endocrine granules in myocardiocytes
Description:
(A): Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy, senium human. A large amount of yellow-brown-stained lipofuscin is present in the vicinity of the nucleus. Note the large nucleus (frequently anisokaryosis).
(B): Cardiocyte in ventricle, electron microscopy, human. Electron-dense granules (dark) of irregular diameter represent lipofuscin in the paranuclear area. Swollen mitochondria and partly disrupted bundles of myofilaments and glycogen surrounding the nucleus are observed (biopsy during open heart operation). Note the banding of the sarcomeres.
(C): Cross-sectioned cardiocytes of the ventricle, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy (swollen interstitium), human. Note irregular outline of the branching and anastomosing cells. Not every cross-sectioned cardiocyte contains a nucleus. Yellow-brown stained pigment is lipofuscin located at the nuclear poles in the cell.
(D): Cardiocyte in ventricle, electron microscopy, monkey. Paranuclearly electron-dense (dark) lipofuscin of varying diameters.
(E): Cardiocyte in atrium, electron microscopy, rat. This special type of myoendocrine cell shows a distinct Golgi area (green encircled) close to the nucleus that reveals few dense secretion granules. These granules will be exported by exocytosis and are known as polypeptides i.a. atrial natriuretic polypeptide (ANP) or BNP (brain natriuretic polypeptide) or CDD (cardiodilatine). (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.06.008). Arrow (black) to lipofuscin and arrows (blue) to lysosomes. (S) Peripheral cytoplasm with caveolae and without myofilaments.
Background: Generally, three cell types are distinguished in the myocardium. (1) Contractile cardiocytes contributing to the pumping action of the heart. (2). Myoendocrine cardiocytes producing polypeptides (e.g. ANP, BNP etc.). (3). Nodal cardiocytes controlling the rhythmic heart contraction, and which are specialised cells found in the sinoatrial node (at the junction right atrium and superior vena cava) as well as in the atrioventricular node (subendocardial in atrial and ventricular septa).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myoendocrine cell, ANP, BNP, lipofuscin, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection