13.1 POJA-L4725+4547
Title: Anulus fibrosus of the heart (human)
Description:
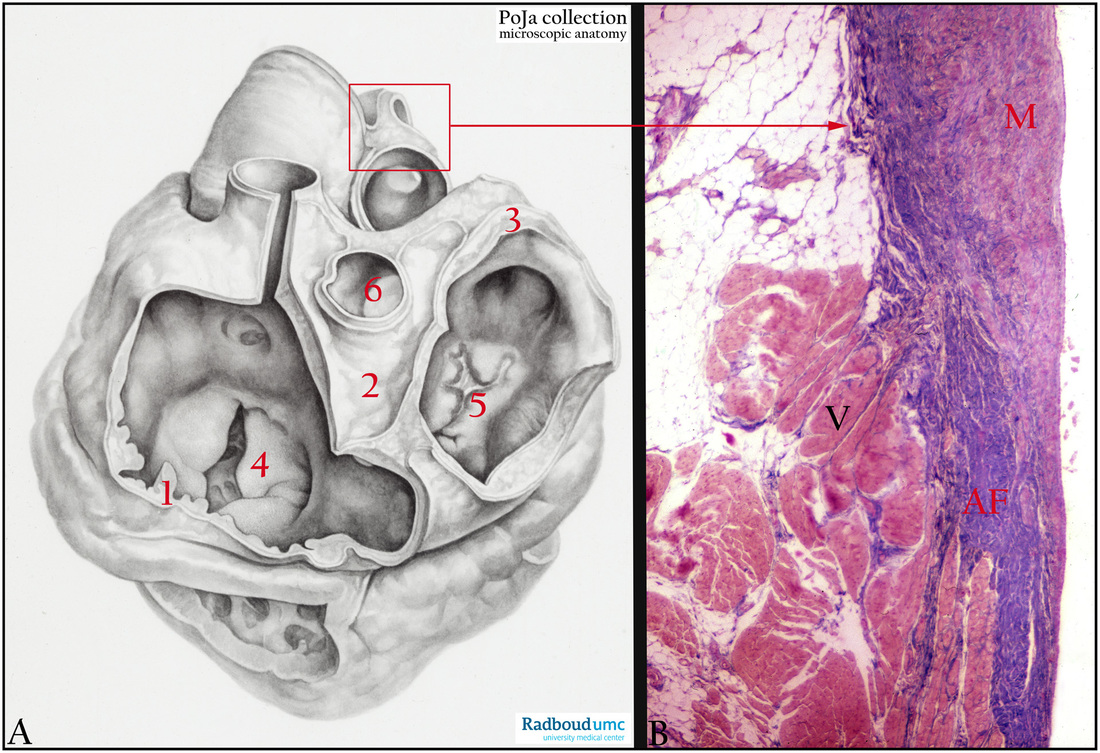
(A): (1) left fibrous ring (anulus fibrosus sinister), (2) right fibrous trigone (trigonum fibrosum dexter), (3) right fibrous ring (anulus fibrosus dexter), (4) mitral valve, (5) tricuspid valve, (6) aortic valve, painted dissection, human.
(B): Heart, root of pulmonary artery and anulus fibrosus, Azan, human. The pulmonary artery is attached to the anulus fibrosus (fibrous skeleton) of the heart and the caudal margin of the anulus adjoins to the myocardium. (M) Media of the artery, (AF) Anulus fibrosus of dense collagen tissue, (V) Myocardium of right ventricular outflow tract.
Background: The anulus fibrosus cordis (fibrous skeleton) is located between atria and ventricles. Synonyms for the anulus are coronary tendon, fibrous ring or Lower’s ring. The skeleton enwraps the atrioventricular and arterial openings of the heart, and connects each of the four valve openings by dense connective tissue. The fibrous skeleton is responsible for sustaining patency of the orifice, it attaches the valve leaflets and it provides origin and insertion to the myocardium.
The anulus fibrosus of the pulmonary root is a tridimensional crown-shaped fibrous structure that is not well-defined. It marks the ventriculo-arterial junction (AF in image B) between the right ventricular infundibulum and the fibroelastic walls in the pulmonary area. (Misfeld M, Sievers H-H. Heart valve macro- and microstructure. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007;362(1484):1421-1436. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2125. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2440405/).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, anulus fibrosus, pulmonary artery, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, histology, POJA collection
Title: Anulus fibrosus of the heart (human)
Description:
(A): (1) left fibrous ring (anulus fibrosus sinister), (2) right fibrous trigone (trigonum fibrosum dexter), (3) right fibrous ring (anulus fibrosus dexter), (4) mitral valve, (5) tricuspid valve, (6) aortic valve, painted dissection, human.
(B): Heart, root of pulmonary artery and anulus fibrosus, Azan, human. The pulmonary artery is attached to the anulus fibrosus (fibrous skeleton) of the heart and the caudal margin of the anulus adjoins to the myocardium. (M) Media of the artery, (AF) Anulus fibrosus of dense collagen tissue, (V) Myocardium of right ventricular outflow tract.
Background: The anulus fibrosus cordis (fibrous skeleton) is located between atria and ventricles. Synonyms for the anulus are coronary tendon, fibrous ring or Lower’s ring. The skeleton enwraps the atrioventricular and arterial openings of the heart, and connects each of the four valve openings by dense connective tissue. The fibrous skeleton is responsible for sustaining patency of the orifice, it attaches the valve leaflets and it provides origin and insertion to the myocardium.
The anulus fibrosus of the pulmonary root is a tridimensional crown-shaped fibrous structure that is not well-defined. It marks the ventriculo-arterial junction (AF in image B) between the right ventricular infundibulum and the fibroelastic walls in the pulmonary area. (Misfeld M, Sievers H-H. Heart valve macro- and microstructure. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007;362(1484):1421-1436. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2125. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2440405/).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, anulus fibrosus, pulmonary artery, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, histology, POJA collection