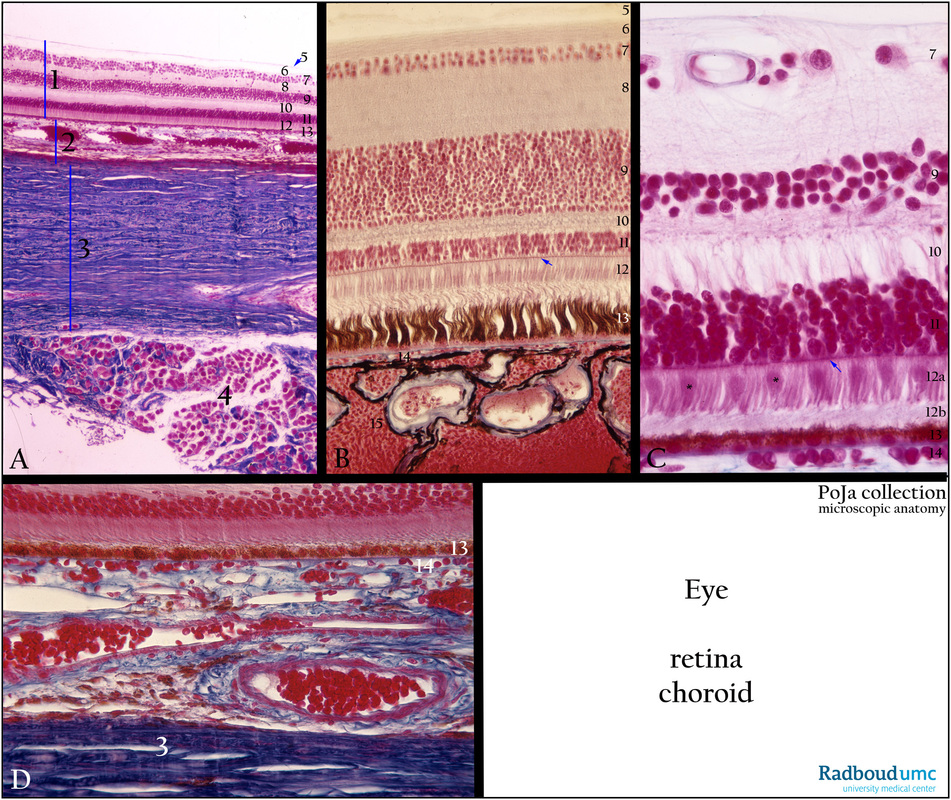
12.1.4 POJA-L2561+3567+4417+2563
Title: Sensory retina with choroid and sclera
Description:
(A): Sensory retina/choroid/sclera/skeletal muscle, stain Azan, human.
(B): Sensory retina/choroid, stain Azan, bird (common tern).
(C): Sensory retina/choriocapillaris, stain Azan, human.
(D): Deeper part of sensory retina/choroid/lamina fusca of sclera, human
(A - D):
(1) Retina.
(2) Choroid.
(3) Sclera.
(4) Extraocular muscle (inferior oblique muscle).
(5) Internal limiting membrane (membrana limitans interna), basal lamina lining the feet of Müller cells.
(6) Optic nerve fibre layer (axons of ganglion cells) with anchoring parts of Müller cells (stratum neurofibrarum).
(7) Ganglion cell layer (stratum ganglionicum nervi optici), being multipolar ganglion cells (3rd neurons of the optic pathway).
(8) Inner plexiform layer (stratum plexiforme internum) containing the synapses between axons of bipolar ganglion cells and dendrites
of multipolar ganglion cells in (8) as well as with amacrine cells.
(9) Inner nuclear layer (2nd neurons of the optic pathway, stratum nucleare internum), containing the nuclei of bipolar ganglion cells, horizontal cells, amacrine cells and Müller cells.
(10) Outer plexiform layer (stratum plexiforme externum), containing the synapses between photoreceptor cells, bipolar ganglion cells
and horizontal cells.
(11) Outer nuclear layer (1st neurons of the optic pathway, stratum neuroepitheliale) with nuclei of the rods and cones.
(12) Inner and outer segments of rods and cones. The arrow (B, C) in layer (12) points to stratum limitans externum (outer limiting membrane), a sieve-like plate formed by the dense junctional complexes and desmosomes of the extensions of the supporting Müller cells with photoreceptor cells.
(12a) Inner segment of the rods and (*) cones (see C).
(12b) Outer segment of the rods and (*) cones (see C).
(13) Pigmented epithelium (stratum pigmentosum retinae). The outer segments of the rods and cone “invade” between the microvilli of
the pigmented epithelial cells.
Remark: The apical processes of the pigmented epithelium in birds (B, 13) are much longer than in human.
(14) Choroid capillary layer (lamina choriocapillaris) is attached to the basal membrane (blue line) of the pigmented epithelial layer just above.
In (D) the rest of the choroid being a vascular layer with numerous wide veins as well as melanocytes (B, 15 and see also A, 2).
Keywords/Mesh: eye, retina, choroid, rod, cone, photoreceptor cell, retina bipolar cell, amacrine cell, retinal ganglion cell, retinal pigment epithelium, histology, POJA collection
Title: Sensory retina with choroid and sclera
Description:
(A): Sensory retina/choroid/sclera/skeletal muscle, stain Azan, human.
(B): Sensory retina/choroid, stain Azan, bird (common tern).
(C): Sensory retina/choriocapillaris, stain Azan, human.
(D): Deeper part of sensory retina/choroid/lamina fusca of sclera, human
(A - D):
(1) Retina.
(2) Choroid.
(3) Sclera.
(4) Extraocular muscle (inferior oblique muscle).
(5) Internal limiting membrane (membrana limitans interna), basal lamina lining the feet of Müller cells.
(6) Optic nerve fibre layer (axons of ganglion cells) with anchoring parts of Müller cells (stratum neurofibrarum).
(7) Ganglion cell layer (stratum ganglionicum nervi optici), being multipolar ganglion cells (3rd neurons of the optic pathway).
(8) Inner plexiform layer (stratum plexiforme internum) containing the synapses between axons of bipolar ganglion cells and dendrites
of multipolar ganglion cells in (8) as well as with amacrine cells.
(9) Inner nuclear layer (2nd neurons of the optic pathway, stratum nucleare internum), containing the nuclei of bipolar ganglion cells, horizontal cells, amacrine cells and Müller cells.
(10) Outer plexiform layer (stratum plexiforme externum), containing the synapses between photoreceptor cells, bipolar ganglion cells
and horizontal cells.
(11) Outer nuclear layer (1st neurons of the optic pathway, stratum neuroepitheliale) with nuclei of the rods and cones.
(12) Inner and outer segments of rods and cones. The arrow (B, C) in layer (12) points to stratum limitans externum (outer limiting membrane), a sieve-like plate formed by the dense junctional complexes and desmosomes of the extensions of the supporting Müller cells with photoreceptor cells.
(12a) Inner segment of the rods and (*) cones (see C).
(12b) Outer segment of the rods and (*) cones (see C).
(13) Pigmented epithelium (stratum pigmentosum retinae). The outer segments of the rods and cone “invade” between the microvilli of
the pigmented epithelial cells.
Remark: The apical processes of the pigmented epithelium in birds (B, 13) are much longer than in human.
(14) Choroid capillary layer (lamina choriocapillaris) is attached to the basal membrane (blue line) of the pigmented epithelial layer just above.
In (D) the rest of the choroid being a vascular layer with numerous wide veins as well as melanocytes (B, 15 and see also A, 2).
Keywords/Mesh: eye, retina, choroid, rod, cone, photoreceptor cell, retina bipolar cell, amacrine cell, retinal ganglion cell, retinal pigment epithelium, histology, POJA collection