5.4.2 POJA-L2349+5010+5016+5033+5030
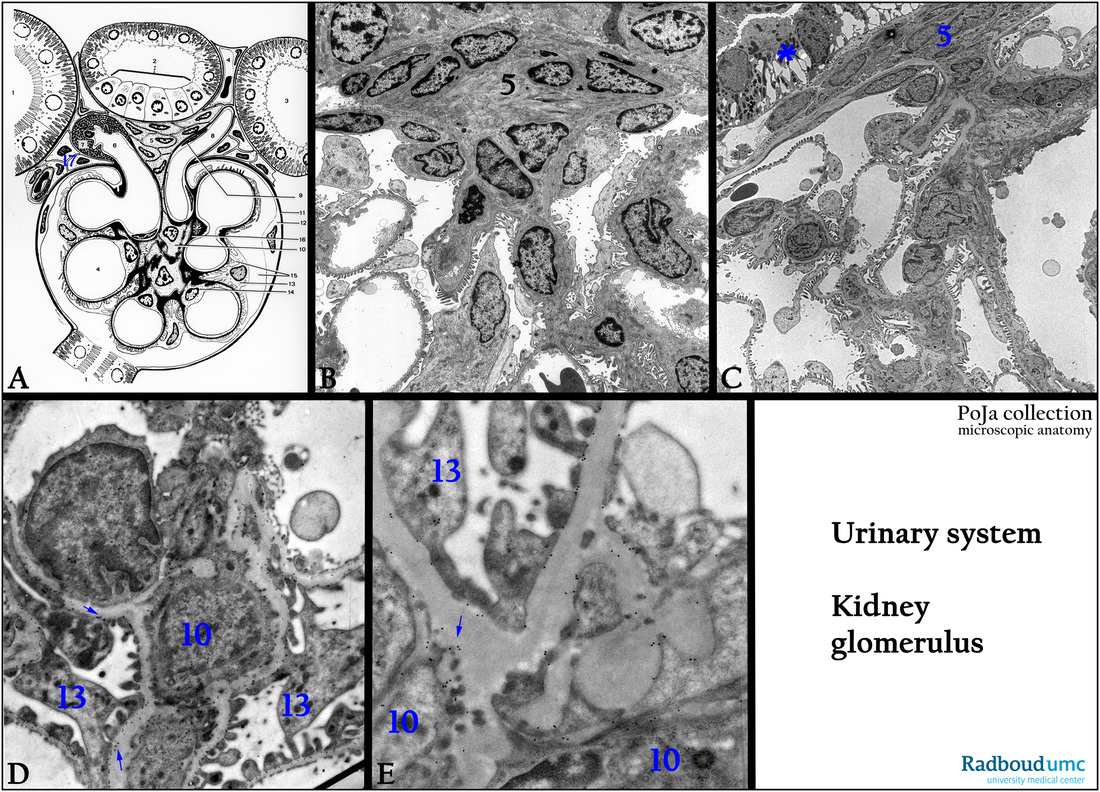
Title: Localization heparan sulfate (HSPG) in glomerulus of kidney XIII
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(1) Pars contorta I (proximal convoluted tubule).
(2) Macula densa (distal tubule, final portion of thick ascending limb).
(3) Pars contorta II (distal convoluted tubule)
(4) Capillary.
(5) Goormaghtigh cells (lacis cells, extraglomerular mesangium cells).
(6) Afferent arteriole.
(7) Granulated juxtaglomerular cell (JG cell).
(8) Efferent arteriole.
(9) Endothelial cell of efferent blood vessel.
(10) Mesangium cell.
(11) Basal membrane of the glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule.
(12) Epithelial cell lining the glomerular capsule.
(13) Podocyte.
(14) Endothelial cell lining a glomerular capillary.
(15) Bowman’s space. (
16) Mesangium matrix continuous with the basal membranes around glomerular capillaries.
(17) Becher’s cells or paraportal cells.
(B): Glomerulus, electron microscopy, rabbit. (black 5) Lacis cells or Goormaghtigh cells, or extraglomerular mesangial cells (also A, 5)
(C): Glomerulus, electron microscopy, rat. (5) Lacis cells (Goormaghtigh cells, extraglomerular measngial cells).
(*) Macula densa cells with widened basal labyrinth.
(D, E): Glomeruli, electron microscopy, rat. Immunogold labeling with antibodies (4C3) and gold particles of 10 nm against heparan sulfate, (arrows) showing the localization of HSPG in the basement membrane material of the mesangial area of the glomerulus.
The labeling is restricted to the cell membranes of the mesangium cells (10) as well as to the mesangial site of the visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) (13).
HSPG in the basal lamina matrix binds to protein ligands and as such regulates processes like blood coagulation, angiogenesis, metastasis and growth of cells.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, mesangium cell, heparan sulfate, lacis cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Localization heparan sulfate (HSPG) in glomerulus of kidney XIII
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(1) Pars contorta I (proximal convoluted tubule).
(2) Macula densa (distal tubule, final portion of thick ascending limb).
(3) Pars contorta II (distal convoluted tubule)
(4) Capillary.
(5) Goormaghtigh cells (lacis cells, extraglomerular mesangium cells).
(6) Afferent arteriole.
(7) Granulated juxtaglomerular cell (JG cell).
(8) Efferent arteriole.
(9) Endothelial cell of efferent blood vessel.
(10) Mesangium cell.
(11) Basal membrane of the glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule.
(12) Epithelial cell lining the glomerular capsule.
(13) Podocyte.
(14) Endothelial cell lining a glomerular capillary.
(15) Bowman’s space. (
16) Mesangium matrix continuous with the basal membranes around glomerular capillaries.
(17) Becher’s cells or paraportal cells.
(B): Glomerulus, electron microscopy, rabbit. (black 5) Lacis cells or Goormaghtigh cells, or extraglomerular mesangial cells (also A, 5)
(C): Glomerulus, electron microscopy, rat. (5) Lacis cells (Goormaghtigh cells, extraglomerular measngial cells).
(*) Macula densa cells with widened basal labyrinth.
(D, E): Glomeruli, electron microscopy, rat. Immunogold labeling with antibodies (4C3) and gold particles of 10 nm against heparan sulfate, (arrows) showing the localization of HSPG in the basement membrane material of the mesangial area of the glomerulus.
The labeling is restricted to the cell membranes of the mesangium cells (10) as well as to the mesangial site of the visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) (13).
HSPG in the basal lamina matrix binds to protein ligands and as such regulates processes like blood coagulation, angiogenesis, metastasis and growth of cells.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, mesangium cell, heparan sulfate, lacis cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection