4.2.1 POJA-L3685+3686
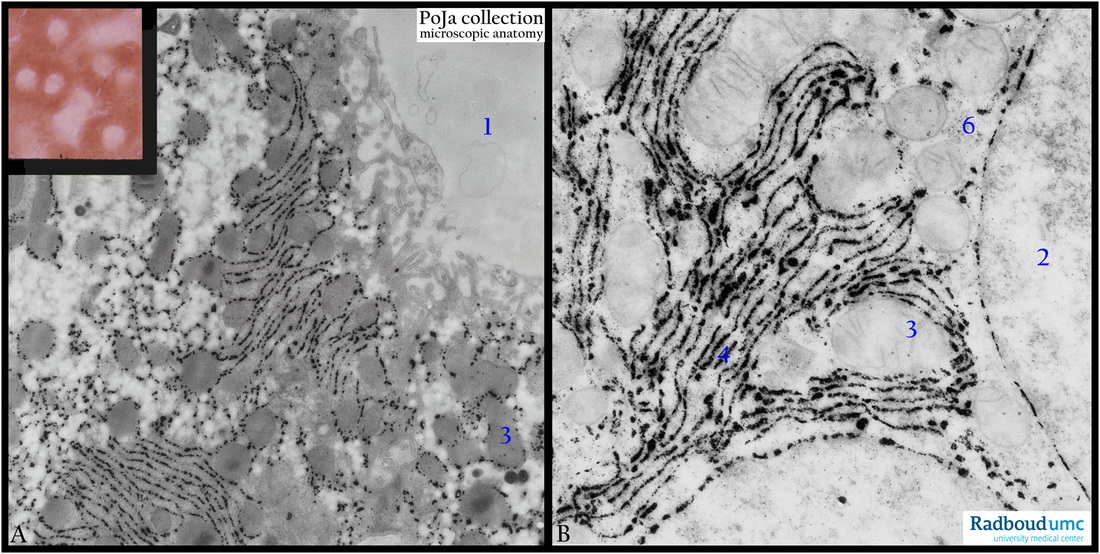
Title: Electron micrograph of glucose-6-phosphatase reaction in liver cell (rat)
Description: Survey (A) and detail (B) of G6Pase reaction in non-contrasted liver cell sections (rat).
(1) Sinusoid.
(2) Nucleus.
(3) Mitochondria.
The enzyme is exactly located in the RER (4)/SER membranes.
(6) Glycogen.
The function of this membrane-bound enzyme associated with the endoplasmic reticulum is to hydrolyze glucose-6-phosphate and create free glucose and a phosphate group. Glucose is then exported via glucose-transporter-membrane proteins from the cell into the blood stream. This catalysis completes the final step in gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. It plays a key role in the homeostatic regulation of blood glucose levels.
The inset in (A) of a diffuse cytoplasmic staining with negative nuclei shows the light microscopical equivalent of the same EM-staining reaction.
Keywords/Mesh: liver cell, RER, SER, glucose-6-phosphatase, glycogen metabolism, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Electron micrograph of glucose-6-phosphatase reaction in liver cell (rat)
Description: Survey (A) and detail (B) of G6Pase reaction in non-contrasted liver cell sections (rat).
(1) Sinusoid.
(2) Nucleus.
(3) Mitochondria.
The enzyme is exactly located in the RER (4)/SER membranes.
(6) Glycogen.
The function of this membrane-bound enzyme associated with the endoplasmic reticulum is to hydrolyze glucose-6-phosphate and create free glucose and a phosphate group. Glucose is then exported via glucose-transporter-membrane proteins from the cell into the blood stream. This catalysis completes the final step in gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. It plays a key role in the homeostatic regulation of blood glucose levels.
The inset in (A) of a diffuse cytoplasmic staining with negative nuclei shows the light microscopical equivalent of the same EM-staining reaction.
Keywords/Mesh: liver cell, RER, SER, glucose-6-phosphatase, glycogen metabolism, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection