7.2 POJA-L1869+1868+1900+1902
Title: Vulva carcinoma (human, adult)
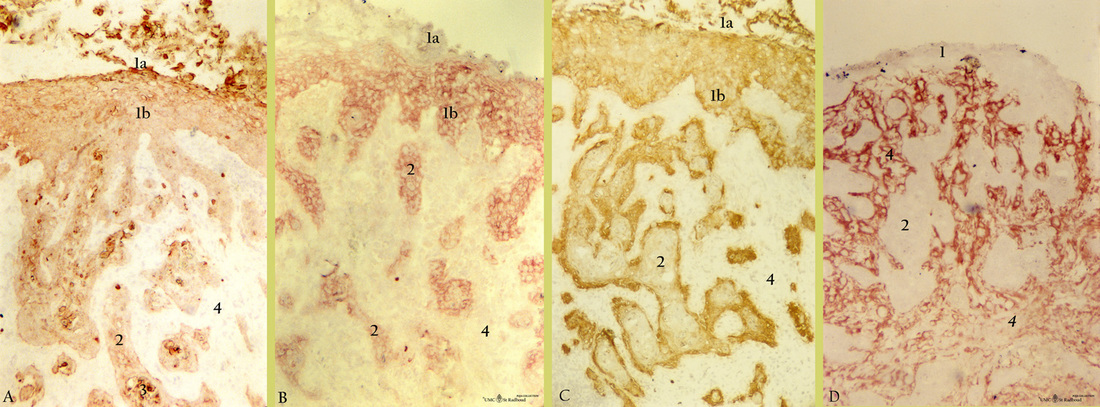
Description: Stain: Imunoperoxidase staining with aminoethylcarbazole (AEC) substrate for antikeratin antibodies OVTL 12-30 and RCK 103 (A-B), anti-endometrial epithelial cells antibody ENDOM 5 as well as anti-connective tissue antibody COLLA (D). Semi-consecutive sections of squamous carcinoma:
(A): Cyokeratin broadly cross-reacting antibody (RCK 103) is weakly expressed in all ingrowing extensions (2) and epithelial layers (1b), but superficial layers (1a) as well as beginning formation of keratin pearls (3) are strong positive.
(B): CK 7 (OVTL 12-30) is expressed by ingrowing extensions (2), basal, parabasal and intermediate layers (1b). However, superficial layers (1a) are CK 7 negative.
(C): Endometrial epithelial cells-specific antibody ENDOM 5 generally stains whole epithelium (1a, 1b) and more intense basal cells. Interestingly, however ingrowing extensions (2) only expressed reactivity in the outer lining (basal cells), but not in the internal epithelial core, confirming distinct differentiation of the tumor cells.
(D): Antibodies (COLLA) to connective tissue components stain only proper lamina (4) and no epithelial structures (1, 2).
Background: 85-90% of vulva carcinomas are invasive squamous cell carcinomas with a mean age of 60-75%. The tumor originates from the epidermis of the vulva tissue and in most cases well differentiated with keratinization. Most lesions involve primarily the labia majora, occasionally the labia minora and introitus. The lesion starts as an induration and progresses to an endophytic ulcer that tends to be unifocal and extends locally, eventually spreading to local inguinal nodes. Human papilloma virus (HPV) plays a role in this process and two types are to be distinguished: non-HPV related (older women, usually keratinizing carcinoma) and HPV-related (younger women with VIN or vulvar intraepithelial neoplasm).
Keywords/Mesh: female reproductive organs, vulva carcinoma, vulvar neoplasms, squamous cell carcinoma, cytokeratins, ENDOM 5, COLLA, histology, POJA collection.
Title: Vulva carcinoma (human, adult)
Description: Stain: Imunoperoxidase staining with aminoethylcarbazole (AEC) substrate for antikeratin antibodies OVTL 12-30 and RCK 103 (A-B), anti-endometrial epithelial cells antibody ENDOM 5 as well as anti-connective tissue antibody COLLA (D). Semi-consecutive sections of squamous carcinoma:
(A): Cyokeratin broadly cross-reacting antibody (RCK 103) is weakly expressed in all ingrowing extensions (2) and epithelial layers (1b), but superficial layers (1a) as well as beginning formation of keratin pearls (3) are strong positive.
(B): CK 7 (OVTL 12-30) is expressed by ingrowing extensions (2), basal, parabasal and intermediate layers (1b). However, superficial layers (1a) are CK 7 negative.
(C): Endometrial epithelial cells-specific antibody ENDOM 5 generally stains whole epithelium (1a, 1b) and more intense basal cells. Interestingly, however ingrowing extensions (2) only expressed reactivity in the outer lining (basal cells), but not in the internal epithelial core, confirming distinct differentiation of the tumor cells.
(D): Antibodies (COLLA) to connective tissue components stain only proper lamina (4) and no epithelial structures (1, 2).
Background: 85-90% of vulva carcinomas are invasive squamous cell carcinomas with a mean age of 60-75%. The tumor originates from the epidermis of the vulva tissue and in most cases well differentiated with keratinization. Most lesions involve primarily the labia majora, occasionally the labia minora and introitus. The lesion starts as an induration and progresses to an endophytic ulcer that tends to be unifocal and extends locally, eventually spreading to local inguinal nodes. Human papilloma virus (HPV) plays a role in this process and two types are to be distinguished: non-HPV related (older women, usually keratinizing carcinoma) and HPV-related (younger women with VIN or vulvar intraepithelial neoplasm).
Keywords/Mesh: female reproductive organs, vulva carcinoma, vulvar neoplasms, squamous cell carcinoma, cytokeratins, ENDOM 5, COLLA, histology, POJA collection.