11.2.2 POJA-L3278+3297+4434+4435+4436+4437
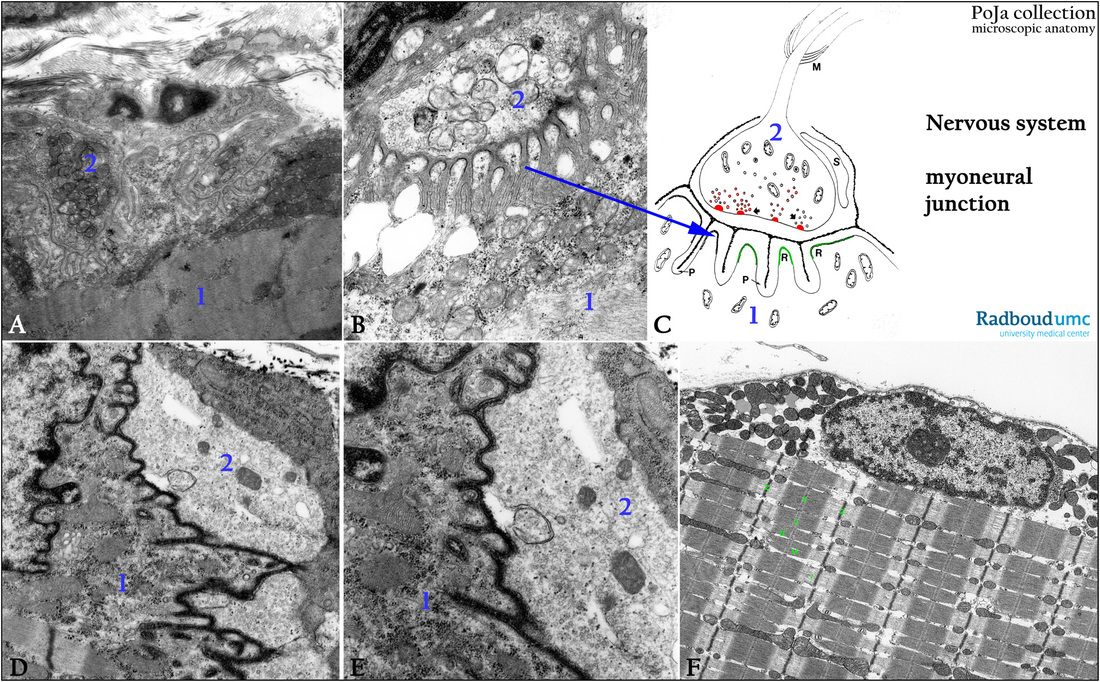
Title: Neuromuscular junction (peripheral ending of effector neuron)
Description:
(A, B): Electron micrographs of neuromuscular junctions with synaptic clefts, soleus muscle, mouse. (1) Striated muscle cell. (2) Efferent nerve terminal and intensely folded synaptic cleft. Note the small presynaptic vesicles in the nerve terminal.
(C): Electron microscopy scheme of neuromuscular junction or motor end plate (peripheral ending of an effector neuron), human. (M) Marks the end of the myelin sheath of the axon. (S) Synapse-associated cell of Schwann without a myelin sheath. The arrows in the “boutons termineaux” point to the grouped transmitter vesicles containing acetylcholine. They are located close to active zones (in red) exactly opposite the deep invading secondary clefts of the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle cell membrane. (P) Represent the invaginations of the sarcolemma. (R) Represent the chemoreceptive surface with acetylcholine-receptors (green).
(D, E): Electron microscopy, tannin–fixed/stained, mouse. Details of the primary and secondary synaptic clefts. Note the numerous transmitter vesicles.
(F): Electron micrograph of gastrocnemius biopsy, human. Striated muscle cell: peripheral nucleus between numerous mitochondria and
few fat droplets. Between the bundles of myofilaments mitochondria are regularly localized.
Background: Sarcomere (S) as a functional unit located between the Z-discs. The A-band (dark) refers to the thick filament band and includes a zone where the thin filaments overlap the thick filaments. The H-zone is the pale staining area within the A-zone, being the
non-overlapping area of the thick filaments. M-line runs in the center of the A-band. I-band (light zone) does not overlap the thick filaments. Thick filaments contain mainly myosin, the thin filaments actin.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, neuromuscular junction, motor end plate, synapse, acetylcholine, striated muscle cell, myosin, actin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Neuromuscular junction (peripheral ending of effector neuron)
Description:
(A, B): Electron micrographs of neuromuscular junctions with synaptic clefts, soleus muscle, mouse. (1) Striated muscle cell. (2) Efferent nerve terminal and intensely folded synaptic cleft. Note the small presynaptic vesicles in the nerve terminal.
(C): Electron microscopy scheme of neuromuscular junction or motor end plate (peripheral ending of an effector neuron), human. (M) Marks the end of the myelin sheath of the axon. (S) Synapse-associated cell of Schwann without a myelin sheath. The arrows in the “boutons termineaux” point to the grouped transmitter vesicles containing acetylcholine. They are located close to active zones (in red) exactly opposite the deep invading secondary clefts of the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle cell membrane. (P) Represent the invaginations of the sarcolemma. (R) Represent the chemoreceptive surface with acetylcholine-receptors (green).
(D, E): Electron microscopy, tannin–fixed/stained, mouse. Details of the primary and secondary synaptic clefts. Note the numerous transmitter vesicles.
(F): Electron micrograph of gastrocnemius biopsy, human. Striated muscle cell: peripheral nucleus between numerous mitochondria and
few fat droplets. Between the bundles of myofilaments mitochondria are regularly localized.
Background: Sarcomere (S) as a functional unit located between the Z-discs. The A-band (dark) refers to the thick filament band and includes a zone where the thin filaments overlap the thick filaments. The H-zone is the pale staining area within the A-zone, being the
non-overlapping area of the thick filaments. M-line runs in the center of the A-band. I-band (light zone) does not overlap the thick filaments. Thick filaments contain mainly myosin, the thin filaments actin.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, neuromuscular junction, motor end plate, synapse, acetylcholine, striated muscle cell, myosin, actin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection