6.1 POJA-L2678+2679+2681+2682
Title: Sertoli cells in testes
Description:
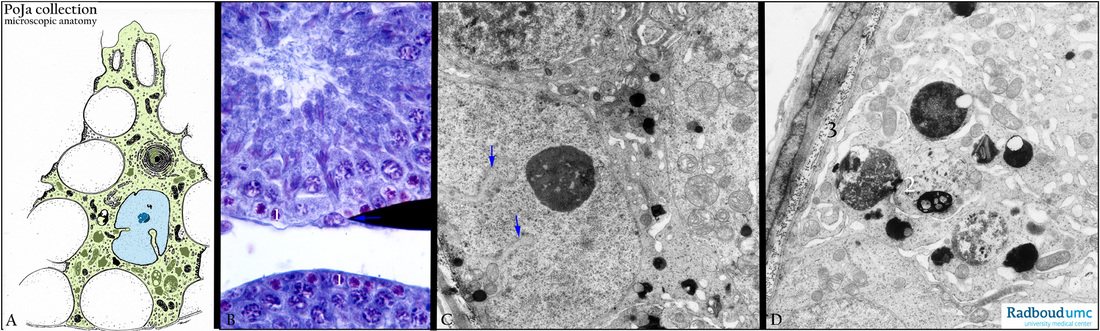
(A) Electron microscopy scheme. (B) Stain methylene blue, mouse. (C, D) Electron microscopy, gerbil.
The Sertoli cell (A) is a supportive cell and covers the seminiferous tubules. They embed all spermatogonia-derived cells, except the spermatogonia (B, 1) themselves, with long finger-like processes. The nucleus shows some invaginations (arrows in A and C), and the nucleolus is prominent visible. The Sertoli cells phagocytose the pinched off cytoplasmic fragments (D, 2) of the spermatocytes and spermatids. (D, 3) Basal lamina, collagen and elastic fibers adjacent to the layers of myoid cells which form the tubular wall of the seminiferous tubules. The Sertoli cells are linked with each other by occluding connections at the basolateral sites in order to protect the differentiating spermatocytes from the blood stream (blood-testis barrier).
Keywords/Mesh: testis, Sertoli cell, spermatogonium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Sertoli cells in testes
Description:
(A) Electron microscopy scheme. (B) Stain methylene blue, mouse. (C, D) Electron microscopy, gerbil.
The Sertoli cell (A) is a supportive cell and covers the seminiferous tubules. They embed all spermatogonia-derived cells, except the spermatogonia (B, 1) themselves, with long finger-like processes. The nucleus shows some invaginations (arrows in A and C), and the nucleolus is prominent visible. The Sertoli cells phagocytose the pinched off cytoplasmic fragments (D, 2) of the spermatocytes and spermatids. (D, 3) Basal lamina, collagen and elastic fibers adjacent to the layers of myoid cells which form the tubular wall of the seminiferous tubules. The Sertoli cells are linked with each other by occluding connections at the basolateral sites in order to protect the differentiating spermatocytes from the blood stream (blood-testis barrier).
Keywords/Mesh: testis, Sertoli cell, spermatogonium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection