11.2.1 POJA-L3186+3188+3054+3055+3303+2977+3201+3204
Title: Ganglion cells and satellite cells
Description:
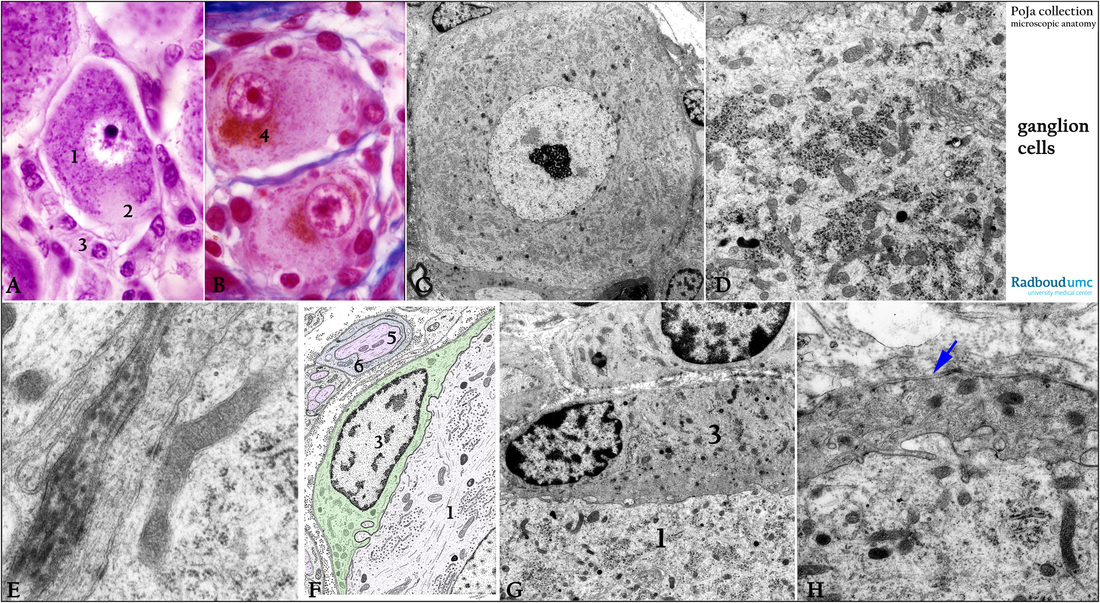
(A): Stain cresyl violet, dog (1) Spinal ganglion cell. (2) Axon hillock devoid of Nissl body. (3) Amphicytes or satellite cells or mantle cells.
(B): Stain Azan, human. Spinal ganglion cell with lipofuscin inclusions (4) which increase at aging.
(C, D): Electron micrograph of a ganglion cell from the sympathetic trunk, rat. The (ortho-) sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of three major parts of the autonomic nervous system (the others being the enteric and parasympathetic systems). The ganglion cell contains an enormous quantity of RER and clusters of ribosomes detailed in (D) and called
Nissl body.
(E): Electron micrograph of satellite cell connected to ganglion cell by small junctions, sympathetic trunk, rabbit.
(F): Electron microscopy scheme of satellite cell (3, green) closely placed next to a ganglion cell (1), human. Note the axons (5, pink) in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells (6).
(G, H): Electron micrograph of satellite cells, spinal ganglions, rat. (G, 1) Ganglion cell. (G, 3) Satellite cell.
Detail of the close “connection” or interaction between ganglion cell and satellite cell (in H).
Note the endosome-derived vesicles, which participate in nerve cell-glia communication as well as basal lamina (arrow) between satellite cell and extracellular matrix.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, ganglion cell, amphicyte, satellite cell, Schwann cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Ganglion cells and satellite cells
Description:
(A): Stain cresyl violet, dog (1) Spinal ganglion cell. (2) Axon hillock devoid of Nissl body. (3) Amphicytes or satellite cells or mantle cells.
(B): Stain Azan, human. Spinal ganglion cell with lipofuscin inclusions (4) which increase at aging.
(C, D): Electron micrograph of a ganglion cell from the sympathetic trunk, rat. The (ortho-) sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of three major parts of the autonomic nervous system (the others being the enteric and parasympathetic systems). The ganglion cell contains an enormous quantity of RER and clusters of ribosomes detailed in (D) and called
Nissl body.
(E): Electron micrograph of satellite cell connected to ganglion cell by small junctions, sympathetic trunk, rabbit.
(F): Electron microscopy scheme of satellite cell (3, green) closely placed next to a ganglion cell (1), human. Note the axons (5, pink) in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells (6).
(G, H): Electron micrograph of satellite cells, spinal ganglions, rat. (G, 1) Ganglion cell. (G, 3) Satellite cell.
Detail of the close “connection” or interaction between ganglion cell and satellite cell (in H).
Note the endosome-derived vesicles, which participate in nerve cell-glia communication as well as basal lamina (arrow) between satellite cell and extracellular matrix.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, ganglion cell, amphicyte, satellite cell, Schwann cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection