5.4.1 POJA-L2526+5008+2476+2475+La0052+2361+La0350
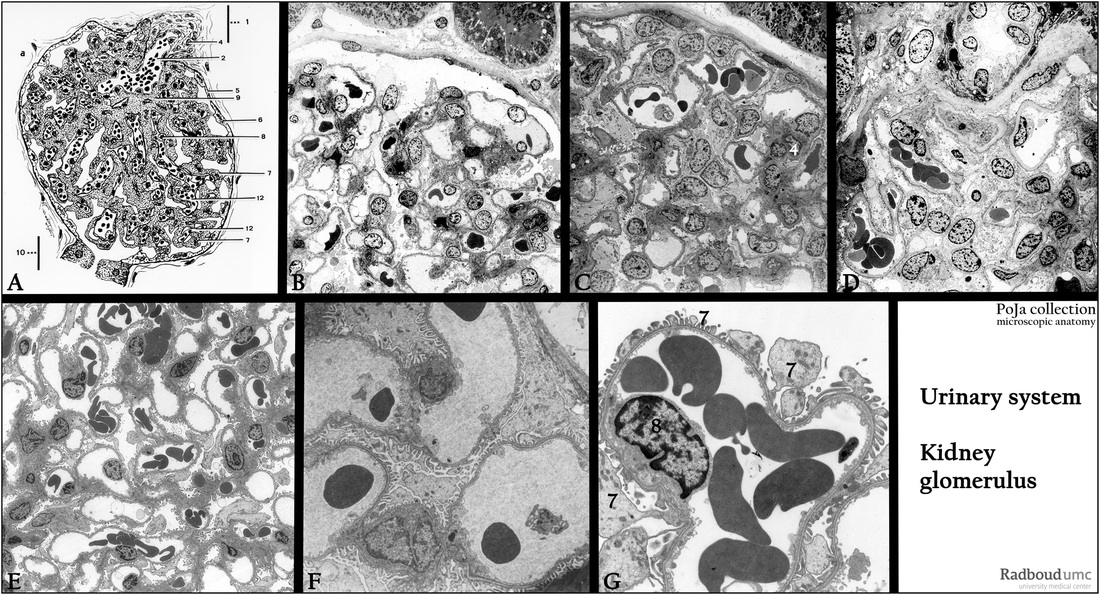
Title: Renal glomerulus (V) in the kidney
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, scheme, human.
(1) Vascular pole. (7) Podocyte (visceral epithelial cell).
(2) Vas afferens or afferent arteriole. (8) Endothelial cell.
(3) Vas efferens. (9) Mesangium cell.
(4) Goormaghtigh cells/extraglomerular mesangium cells (lacis cells). (10) Urinary pole, (proximal convoluted tubule, pars contorta I).
(5) Bowman’s capsule. (11) Bowman’s space.
(6) Epithelial (parietal) cell of the glomerular capsule. (12) Capillary.
(B, C, D): Survey glomeruli, electron microscopy, human. Illustrating the items mentioned in (A).
(E, F, G): Glomerular capillary networks, electron microscopy, rat. Details the capillaries in the glomerulus (G). The foot processes
of the podocyte (7) are wrapped around the capillary leaving filtration slit pores between adjacent foot processes.
(8) Endothelial cell lining the capillary.
Background: Generally there are minor differences between human and rodent glomeruli, dependent on age, diet etc.
In the human glomerulus the Bowman’s capsule is thicker partly due to layered basal lamina surrounding the parietal cells.
The mesangial matrix is more extensive, denser and irregular, while the basal laminae around the glomerular capillaries are thicker
and often irregular. Visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) are numerous, with several swollen cell bodies, irregular-shaped with
different shaped foot processes onto the thick basal laminae of capillaries.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, podocyte, capillary, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Renal glomerulus (V) in the kidney
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, scheme, human.
(1) Vascular pole. (7) Podocyte (visceral epithelial cell).
(2) Vas afferens or afferent arteriole. (8) Endothelial cell.
(3) Vas efferens. (9) Mesangium cell.
(4) Goormaghtigh cells/extraglomerular mesangium cells (lacis cells). (10) Urinary pole, (proximal convoluted tubule, pars contorta I).
(5) Bowman’s capsule. (11) Bowman’s space.
(6) Epithelial (parietal) cell of the glomerular capsule. (12) Capillary.
(B, C, D): Survey glomeruli, electron microscopy, human. Illustrating the items mentioned in (A).
(E, F, G): Glomerular capillary networks, electron microscopy, rat. Details the capillaries in the glomerulus (G). The foot processes
of the podocyte (7) are wrapped around the capillary leaving filtration slit pores between adjacent foot processes.
(8) Endothelial cell lining the capillary.
Background: Generally there are minor differences between human and rodent glomeruli, dependent on age, diet etc.
In the human glomerulus the Bowman’s capsule is thicker partly due to layered basal lamina surrounding the parietal cells.
The mesangial matrix is more extensive, denser and irregular, while the basal laminae around the glomerular capillaries are thicker
and often irregular. Visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) are numerous, with several swollen cell bodies, irregular-shaped with
different shaped foot processes onto the thick basal laminae of capillaries.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, podocyte, capillary, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection