5.7 POJA-La0077+La0078+La0092+L2428+2429
Title: Transitional epithelium of the urinary bladder 5
Description:
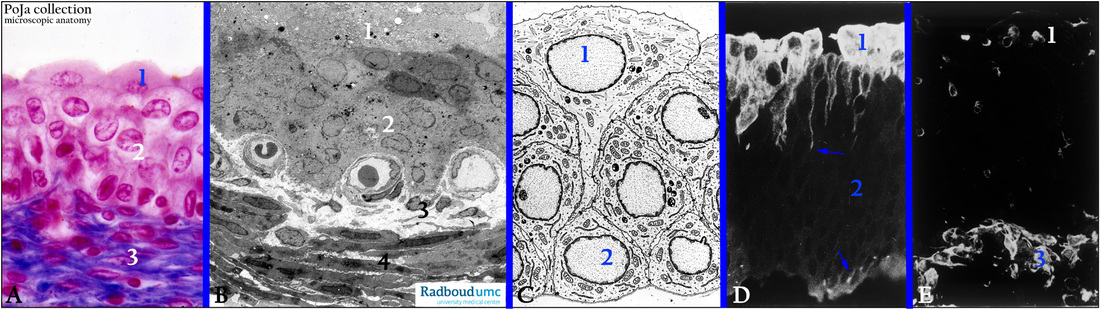
(A): Urothelium, stain Azan, human. (1) Surface epithelial cells (facet cells) or umbrella-like epithelial cells. (2) Intermediate epithelial cells.
(3) Connective tissue cells of the lamina propria.
(B): Electron micrograph of a similar area as in (A), gerbil. Note the presence of small capillaries adjacent to the basal epithelial cells
just above the fibroblasts (3) and smooth muscle cells of the inner muscularis (4).
(C): Electron microscopy scheme with surface epithelial cells (1) and basal cells (2), human. Note that the superficial cells are connected to the basal layers via long slender processes which are also partly visualized in (D). The superficial cells display a dense network of apically localized intermediate filaments (extensibility) and glycoproteins (water impermeability).
(D): The fluorescent anti-keratin 18 antibody (RGE53) selectively stains here the superficial epithelial cells and their processes (arrows), and not all other epithelial cells (2), human.
(E): The fluorescent anti-vimentin antibody leaves the epithelium unstained in contrast to the fibroblasts of the lamina propria (3), human.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, urinary bladder, vesica urinaria, urothelium, transitional epithelium, cytokeratin, vimentin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Transitional epithelium of the urinary bladder 5
Description:
(A): Urothelium, stain Azan, human. (1) Surface epithelial cells (facet cells) or umbrella-like epithelial cells. (2) Intermediate epithelial cells.
(3) Connective tissue cells of the lamina propria.
(B): Electron micrograph of a similar area as in (A), gerbil. Note the presence of small capillaries adjacent to the basal epithelial cells
just above the fibroblasts (3) and smooth muscle cells of the inner muscularis (4).
(C): Electron microscopy scheme with surface epithelial cells (1) and basal cells (2), human. Note that the superficial cells are connected to the basal layers via long slender processes which are also partly visualized in (D). The superficial cells display a dense network of apically localized intermediate filaments (extensibility) and glycoproteins (water impermeability).
(D): The fluorescent anti-keratin 18 antibody (RGE53) selectively stains here the superficial epithelial cells and their processes (arrows), and not all other epithelial cells (2), human.
(E): The fluorescent anti-vimentin antibody leaves the epithelium unstained in contrast to the fibroblasts of the lamina propria (3), human.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, urinary bladder, vesica urinaria, urothelium, transitional epithelium, cytokeratin, vimentin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection