5.7 POJA-L5032+5039
Title: Interstitial cells in suburothelial layer of the human urinary bladder 4
Description:
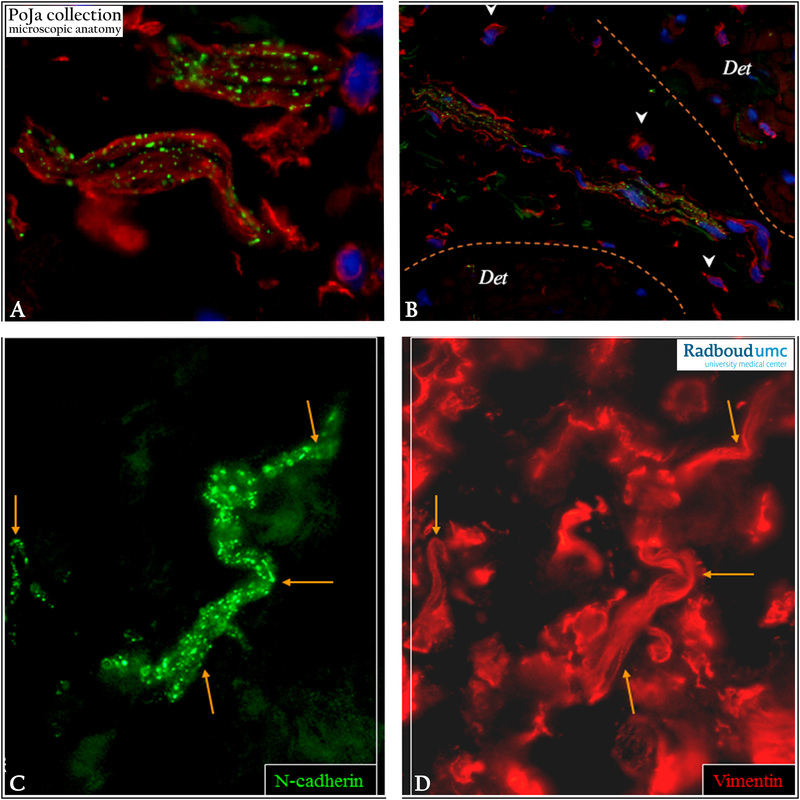
Immunofluorescence staining of interstitial cells in the suburothelial layer with antibodies against N-cadherin (green) and vimentin (red). (A): Note the punctate pattern of N-cadherin in contrast to the vimentin+ filaments which both are expressed within the same cell body.
(B): Multiple elongated N-cadherin+/vimentin+ containing cells are closely associated with at the border of detrusor smooth muscle bundles. Arrowheads show small vimentin+ cells with little perinuclear cytoplasm, highly resembling regular fibroblasts.
(C, D): Punctated expression of N-cadherin in (C) that is located at the cell membrane of some vimentin+ cells. Vimentin (D) shows a filamentous staining pattern. Both are expressed within the same cell body (C, D).
Cells expressing vimentin but lacking expression of N-cadherin embody fibroblasts.
Vimentin stains all fibroblastic cells while N-cadherin exclusively highlights the interstitial cell types showing a punctate pattern (A, C).
Multiple elongated N-cadherin+/vimentin+ containing interstitial cells are closely associated at the border of the detrusor (Det in B) smooth muscle bundles. They are thought to be a subpopulation of interstitial cells in the human bladder, i.e. a myofibroblast-like
cell type. It is thought that these interstitial cells are involved in the local contractions of the bladder
(A - D, by courtesy of K.A.J. Kuijpers, MD PhD, Department of Urology, Radboud university medical center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, urinary bladder, vesica urinaria, interstitial cell, N-cadherin, vimentin, histology, POJA collection
Title: Interstitial cells in suburothelial layer of the human urinary bladder 4
Description:
Immunofluorescence staining of interstitial cells in the suburothelial layer with antibodies against N-cadherin (green) and vimentin (red). (A): Note the punctate pattern of N-cadherin in contrast to the vimentin+ filaments which both are expressed within the same cell body.
(B): Multiple elongated N-cadherin+/vimentin+ containing cells are closely associated with at the border of detrusor smooth muscle bundles. Arrowheads show small vimentin+ cells with little perinuclear cytoplasm, highly resembling regular fibroblasts.
(C, D): Punctated expression of N-cadherin in (C) that is located at the cell membrane of some vimentin+ cells. Vimentin (D) shows a filamentous staining pattern. Both are expressed within the same cell body (C, D).
Cells expressing vimentin but lacking expression of N-cadherin embody fibroblasts.
Vimentin stains all fibroblastic cells while N-cadherin exclusively highlights the interstitial cell types showing a punctate pattern (A, C).
Multiple elongated N-cadherin+/vimentin+ containing interstitial cells are closely associated at the border of the detrusor (Det in B) smooth muscle bundles. They are thought to be a subpopulation of interstitial cells in the human bladder, i.e. a myofibroblast-like
cell type. It is thought that these interstitial cells are involved in the local contractions of the bladder
(A - D, by courtesy of K.A.J. Kuijpers, MD PhD, Department of Urology, Radboud university medical center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, urinary bladder, vesica urinaria, interstitial cell, N-cadherin, vimentin, histology, POJA collection