5.4.2 POJA-L2432+5010+2335+2347+2350
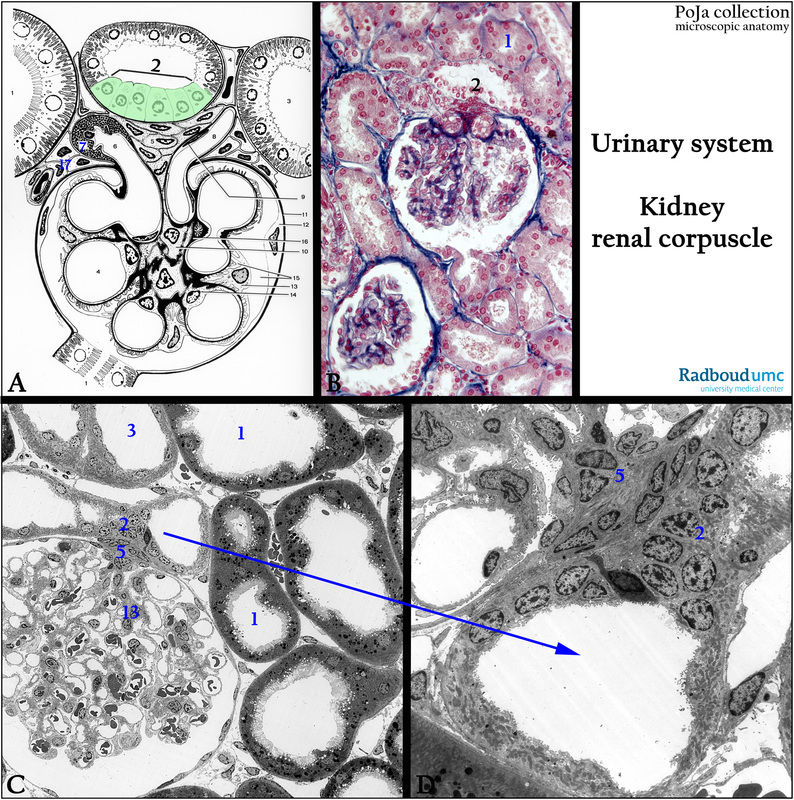
Title: Renal corpuscle in kidney: macula densa I
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(1) Pars contorta I (proximal convoluted tubule).
(2) Macula densa (light green) (distal tubule, final portion of thick ascending limb).
(3) Pars contorta II (distal convoluted tubule)
(4) Capillary.
(5) Goormaghtigh cells (lacis cells, extraglomerular mesangium cells).
(6) Afferent arteriole.
(7) Granulated juxtaglomerular cell (JG cell).
(8) Efferent arteriole.
(9) Endothelial cell of efferent blood vessel.
(10) Mesangium cell.
(11) Basal membrane of the glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule.
(12) Epithelial cell lining the glomerular capsule.
(13) Podocyte.
(14) Endothelial cell lining a glomerular capillary.
(15) Bowman’s space.
(16) Mesangium matrix continuous with the basal membranes around glomerular capillaries.
(17) Becher’s cells or paraportal cells.
(B): Glomerulus, stain Azan, human. Compare with (A).
(C, D): Electron microscopy of glomerulus, perfusion-fixed, rabbit. (2) Is in the proximity of the macula densa.
The macula densa is a specialized part of the distal tubule being in close “contact” with the afferent vessel of the glomerulus.
These cells monitor the NaCl ions in the liquid in the distal tubules.
The lacis cells (or Goormaghtigh cells) also known as extraglomerular mesangium cells are considered as an extramesangial network continuous with the mesangium cells in the glomerulus.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, macula densa, podocyte, Goormaghtigh cell, lacis cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Renal corpuscle in kidney: macula densa I
Description:
(A): Glomerulus, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(1) Pars contorta I (proximal convoluted tubule).
(2) Macula densa (light green) (distal tubule, final portion of thick ascending limb).
(3) Pars contorta II (distal convoluted tubule)
(4) Capillary.
(5) Goormaghtigh cells (lacis cells, extraglomerular mesangium cells).
(6) Afferent arteriole.
(7) Granulated juxtaglomerular cell (JG cell).
(8) Efferent arteriole.
(9) Endothelial cell of efferent blood vessel.
(10) Mesangium cell.
(11) Basal membrane of the glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule.
(12) Epithelial cell lining the glomerular capsule.
(13) Podocyte.
(14) Endothelial cell lining a glomerular capillary.
(15) Bowman’s space.
(16) Mesangium matrix continuous with the basal membranes around glomerular capillaries.
(17) Becher’s cells or paraportal cells.
(B): Glomerulus, stain Azan, human. Compare with (A).
(C, D): Electron microscopy of glomerulus, perfusion-fixed, rabbit. (2) Is in the proximity of the macula densa.
The macula densa is a specialized part of the distal tubule being in close “contact” with the afferent vessel of the glomerulus.
These cells monitor the NaCl ions in the liquid in the distal tubules.
The lacis cells (or Goormaghtigh cells) also known as extraglomerular mesangium cells are considered as an extramesangial network continuous with the mesangium cells in the glomerulus.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, macula densa, podocyte, Goormaghtigh cell, lacis cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection