13.1 POJA-L4735C+4729B+4503+4537+4501+4502
Title: Macroscopy, microscopy and scheme of the heart
Description:
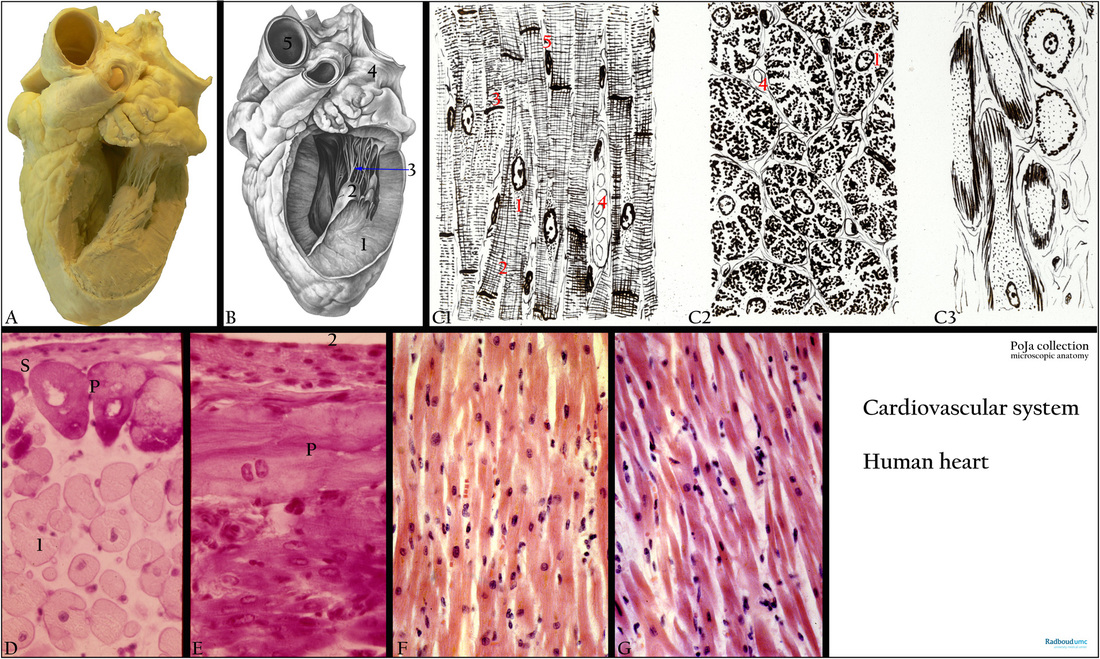
(A-B): Macroscopy of opened left ventricle of the heart. Left ventricle (1), papillary muscle (2), chordae tendinae (arrow 3), auricle (4), aorta (5).
(C1-3): Scheme cardiocytes, longitudinally (C1) and cross-sectioned (C2). Modified cardiocytes of the conducting system (C3, Purkinje fibres). Perinuclear space (1). There are no fibrils in the perinuclear space. Branching of a cardiomyocyte (2). Intercalated disc (3). Venule or capillary with erythrocytes (4). Nucleus of fibroblast (5). In contrast to skeletal muscles, the cardiac muscle fibres are branched and anastomose with each other, thus creating a network. The Purkinje fibres (C3) are modified muscle fibres serving for excitation and conduction.
(D, E): Heart, ventricle, conducting system, PAS and Haematoylin-eosin, human. Specialised modified cardiomyocytes in branches of the conducting system also referred as Purkinje fibres (P). These cask-like cells are PAS positive (cross-sectioned) and are located below the subendocardial tissue
(S). (1) Normal cardiocytes. (2) Lumen ventricle.
(F): Cardiocytes of ventricle, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy human. Compare to atrial cardiocytes in (G).
(G): Cardiac cells (cardiocytes) of atrium, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy human. The atrial cells are smaller than the ventricular cells. There is distension between the cells due to fluid accumulation (autopsy preparation).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, papillary muscle, myocardiocyte, Purkinje fibre, conducting system, histology, POJA collection
Title: Macroscopy, microscopy and scheme of the heart
Description:
(A-B): Macroscopy of opened left ventricle of the heart. Left ventricle (1), papillary muscle (2), chordae tendinae (arrow 3), auricle (4), aorta (5).
(C1-3): Scheme cardiocytes, longitudinally (C1) and cross-sectioned (C2). Modified cardiocytes of the conducting system (C3, Purkinje fibres). Perinuclear space (1). There are no fibrils in the perinuclear space. Branching of a cardiomyocyte (2). Intercalated disc (3). Venule or capillary with erythrocytes (4). Nucleus of fibroblast (5). In contrast to skeletal muscles, the cardiac muscle fibres are branched and anastomose with each other, thus creating a network. The Purkinje fibres (C3) are modified muscle fibres serving for excitation and conduction.
(D, E): Heart, ventricle, conducting system, PAS and Haematoylin-eosin, human. Specialised modified cardiomyocytes in branches of the conducting system also referred as Purkinje fibres (P). These cask-like cells are PAS positive (cross-sectioned) and are located below the subendocardial tissue
(S). (1) Normal cardiocytes. (2) Lumen ventricle.
(F): Cardiocytes of ventricle, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy human. Compare to atrial cardiocytes in (G).
(G): Cardiac cells (cardiocytes) of atrium, Haematoxylin-eosin, autopsy human. The atrial cells are smaller than the ventricular cells. There is distension between the cells due to fluid accumulation (autopsy preparation).
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, atrium, ventricle, valve, papillary muscle, myocardiocyte, Purkinje fibre, conducting system, histology, POJA collection